What Is Proprioception & Simple Ways to Improve It
Did you know that contrary to popular belief, you actually have seven senses?
Sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing play important roles in developing your brain and nervous system -- but they’re only part of the story.
The two senses that often go unrecognized are your proprioception and vestibular system.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is proprioception?
How does proprioception work?
Symptoms of proprioceptive disorder
How to strengthen proprioception from the comfort of your home
What Is Proprioception?
Proprioception, often considered the “sixth sense,” is your sense of body position and movement in space. In fact, the Latin meaning of proprioception is “the unconscious perception of movement.”
It’s your proprioception that allows you to move around freely without having conscious awareness of it. For instance, your ability to brush your hair without seeing the back of your head or walking around without looking at your feet are two perfect examples of proprioception at work[*].
Anatomy Of Proprioception
So, how exactly does proprioception work?
Your ability to sense where your body is in space results from sensory receptors in your body, mostly located in your muscles, skin, and joints. These receptors send signals to your nervous system and brain, telling them where your body is and what movements are happening. Your brain and nervous system then process this information, and you respond accordingly[*][*].
For many people, the sense of proprioception goes unrecognized for most of your life. It’s just one of the many wonders of the human body that works seamlessly without conscious thought.
When issues arise with your sense of proprioception, however, life can become a lot more difficult.
Proprioception Disorder
Issues with proprioception can result from a range of conditions, including[*]:
Sensory Processing Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Brain injury
ALS
Parkinson’s Disease
Huntington’s Disease
Stroke
Peripheral neuropathy
And more
When your proprioception system isn’t functioning optimally, your ability to recognize where your body is and how its moving is altered. Some symptoms of proprioception disorders include:
Balance issues, such as falling easily and not being able to stand on one foot.
Clumsiness, such as walking into things and dropping items.
Coordination issues, such as the inability to walk in a straight line.
Fear of falling or losing balance, often resulting in avoidance of activities.
Inability to sense your own strength or weakness.
Poor posture and slouching.
On the surface, it may appear that issues with proprioception primarily impact your physical abilities. The truth, however, is that proprioception has a wide-reaching effect on your entire system.
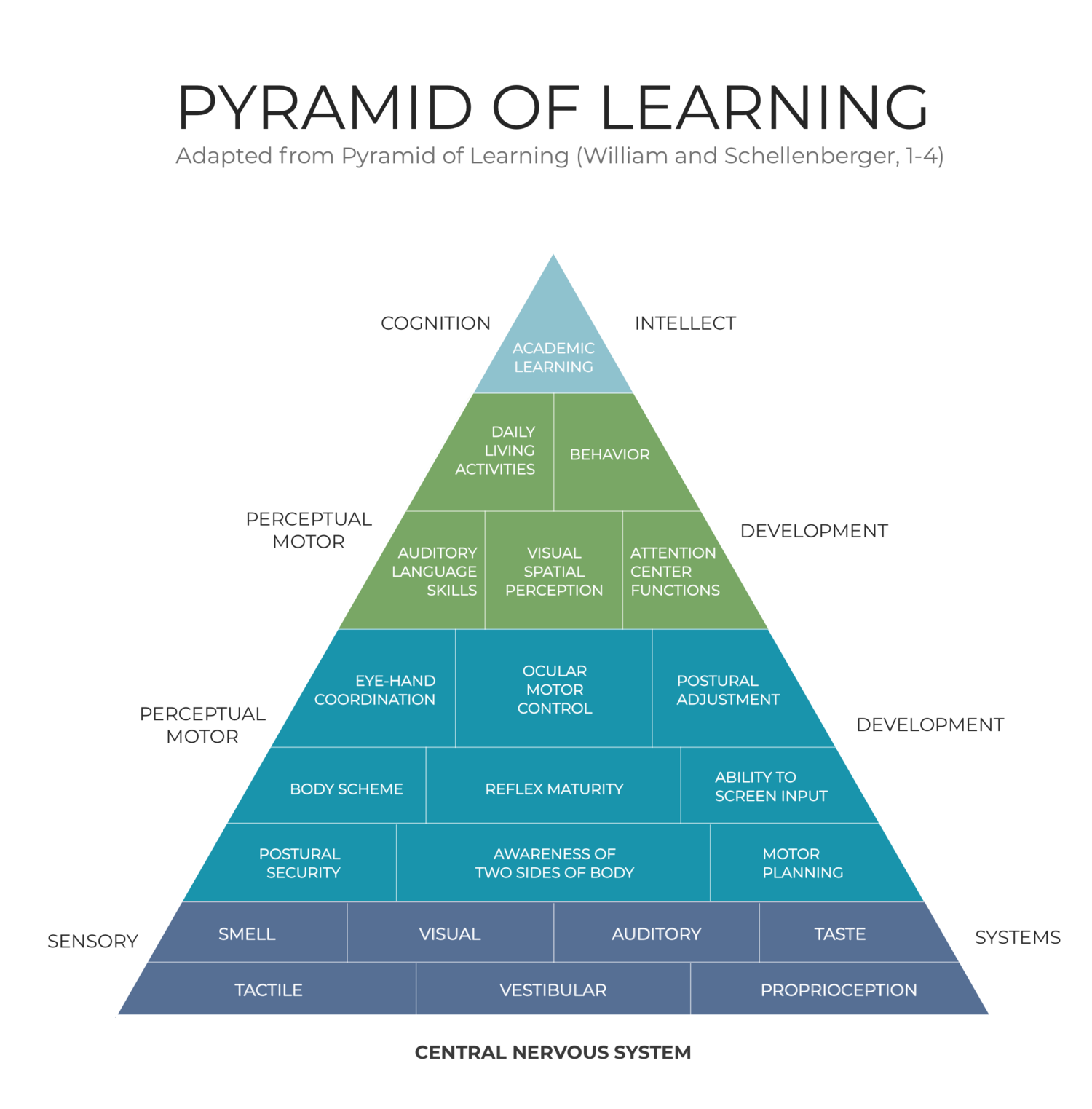
Your senses (including proprioception) set the foundation for all other cognitive, emotional, and physical regulation. Through input that you receive from your senses, your brain and body can signal to each other what’s happening in the world around you and then set the stage for deeper learning and interactions in the world.
As mentioned previously, the five-senses model is outdated at this point. We now understand that beyond sight, smell, taste, hearing, and touch, there are two more senses that provide vital information for the mind and body -- proprioception and the vestibular system.
Therefore, poorly functioning proprioception will impact all upstream processes having to do with behavior, learning, emotional regulation, language and auditory skills, eye-hand coordination, etc.
This is why strengthening proprioception can have numerous positive effects and is one of the primary areas that we work on at Brain Harmony.
The image below illustrates the crucial nature of all seven senses and the upstream impact they have on your body and mind.
How To Strengthen Proprioception At Home
At Brain Harmony, we use a 5-step process that strengthens the pyramid of learning depicted above. Listening systems like the Safe and Sound Protocol (SSP) and Focus Unit make up some of our foundational work -- but at-home exercises like those outlined below are equally as vital to building the tools necessary for optimal cognitive development and emotional control.
Depending on your schedule, lifestyle, and what you have available to you, any of the following proprioception exercises may be used to strengthen your sixth sense.
Recreation and Movement
Exercise and movement are vital to overall health and wellbeing. Along with the many health benefits associated with exercise, you’ll also be working your proprioception “muscle” when you engage in any of the following:
Running
Jogging
Fast walking
Jumping on a trampoline
Biking
Climbing
Rowing a boat, kayak, or canoe
Swimming
Playing sports
Hiking uphill
Martial arts
Boxing
Skiing (water skiing, cross country)
Yoga
Free weights
Medicine ball exercise
Leisurely Activities
Aside from activities that fall under exercise, there are other ways to strengthen proprioception with fun or leisurely activities.
Some leisurely activities include:
Squeezing a stress ball
Making a snowman
Giving or receiving bear hugs
Progressive muscle relaxation
Using a weighted blanket or other weighted objects like a vest or lap pad
Getting a deep massage
Giving a child a piggyback ride
Home and Yard Work
For those of you that may not have time to dedicate to working out or leisurely movement, you can still strengthen proprioception while engaging in basic home cleaning and yard work.
Some examples include:
Shoveling snow or gravel
Washing your car
Vacuuming or mopping your floor
Raking leaves
Stacking firewood
Pushing a lawnmower
Using a wheelbarrow
Carrying in groceries and putting them away
Rearranging furniture
Sruccing cleaning tasks
Taking trash cans out
Doing laundry (carrying the basket, transferring wet clothes to the dryer, hanging wet clothes)
Washing windows
Organizing pots and pans
Gardening (pulling weeds, planting, digging, watering)
Food And Drink
You can even activate proprioception through simple activities like chewing and drinking.
Examples include:
Drinking a thick milkshake or smoothie through a straw
Chewing gum
Eating crunchy foods like carrots, celery, jerky, or pretzels
Chewable jewelry
Do You Need To Strengthen Your Proprioception?
If you feel that you or a loved one is struggling with issues around proprioception, you may want to work with an occupational therapist for more guided therapies.
At Brain Harmony, we recognize that cognitive development, emotional control, and physical abilities all stem from our foundational need to use our senses optimally. If any of our senses are off-kilter, the upstream processes will suffer.
While all of the above exercises are excellent ways to strengthen proprioception, they’re only one piece to the larger puzzle that makes up a highly functioning nervous system.
For more information about how Brain Harmony works, and if this is the right program for you, contact us today for a Free Consultation.